Sandwich layering in binary nanoparticle films and effect of size ratio on stratification behavior
Citation
Liu, W.; Carr, A.J.; Yager, K.G.; Routh, A.F.; Bhatia, S.R. "Sandwich layering in binary nanoparticle films and effect of size ratio on stratification behavior"
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2019,
538 209–217.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.11.084Summary
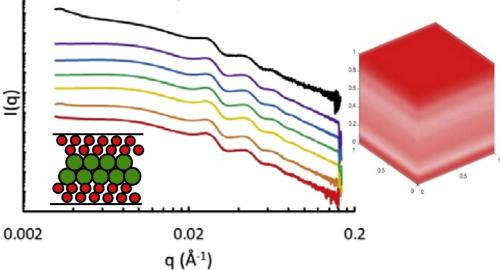
SAXS is used to study the organizing of different sized colloids during drying. Particles of different size can segregate vertically during drying; which can lead to the formation of sandwich structures.
Abstract
SAXS spectra showed noticeable variations at different film depths, consistent with stratification. These results are quantified to obtain vertical composition profiles. We observe “sandwich”-type layered structures at different nanoparticle size ratios, which to our knowledge have not been previously observed experimentally or predicted by theory. For example, for films of larger particle size ratios (7.7–4.8), large particles are enriched at the film top and bottom, leading to a large-small-large or “LSL” behavior; while within films of smaller particle size ratio (2.2–1.2), small particles are enriched at the top and bottom of the film (small-large-small or “SLS” structures). The enrichment of particles at the top persists over several hundred particle layers and is not just a single monolayer pinned to the upper surface.