Self-assembly of single dielectric nanoparticle layers and integration in polymer-based solar cells
Citation
Allen, J.E.; Ray, B.; Khan, M.R.; Yager, K.G.; Alam, M.A.; Black, C.T. "Self-assembly of single dielectric nanoparticle layers and integration in polymer-based solar cells"
Applied Physics Letters 2012,
101 063105.
doi: 10.1063/1.4744928Summary
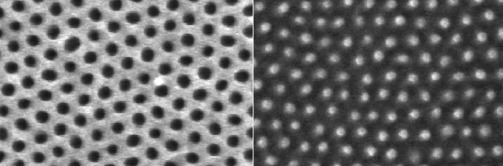
We describe how self-assembly can be used to generate a dielectric layer of alumina nanoparticles for use in solar cell applications. Performance is increased by both light diffusion and increase in electrode contact area.
Abstract
A single, self-assembled layer of highly uniform dielectric alumina nanoparticles improves the photovoltaic performance of organic semiconductor bulk heterojunction solar cells. The block copolymer based self-assembly approach is readily amenable to the large areas required for solar cell fabrication. A fraction of the performance gain results from incident light scattering which increases active layer absorption and photocurrent output, consistent with device simulations. The nanoparticle layer also roughens the device electrode surface, increasing contact area and improving device fill factor through more efficient charge collection.

