Linking Group Influences Charge Separation and Recombination in All-Conjugated Block Copolymer Photovoltaics
Citation
Mok, J.W.; Lin, Y.-H.; Yager, K.G.; Mohite, A.D.; Nie, W.; Darling, S.B.; Lee, Y.; Gomez, E.; Gosztola, D.; Shcaller, R.D.; Verduzco, R. "Linking Group Influences Charge Separation and Recombination in All-Conjugated Block Copolymer Photovoltaics"
Advanced Functional Materials 2015,
25 5578–5585.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201502623Summary
We study how the inter-block linking group in an all-conjugate block-copolymer affects the photovoltaic performance.
Abstract
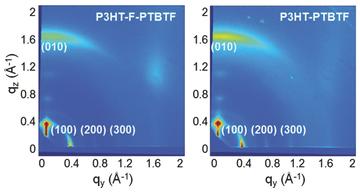
All-conjugated block copolymers bring together hole- and electron-conductive polymers and can be used as the active layer of solution-processed photovoltaic devices, but it remains unclear how molecular structure, morphology, and electronic properties influence performance. Here, the role of the chemical linker is investigated through analysis of two donor–linker–acceptor block copolymers that differ in the chemistry of the linking group. Device studies show that power conversion efficiencies differ by a factor of 40 between the two polymers, and ultrafast transient absorption measurements reveal charge separation only in block copolymers that contain a wide bandgap monomer at the donor–acceptor interface. Optical measurements reveal the formation of a low-energy excited state when donor and acceptor blocks are directly linked without this wide bandgap monomer. For both samples studied, it is found that the rate of charge recombination in these systems is faster than in polymer–polymer and polymer–fullerene blends. This work demonstrates that the linking group chemistry influences charge separation in all-conjugated block copolymer systems, and further improvement of photovoltaic performance may be possible through optimization of the linking group. These results also suggest that all-conjugated block copolymers can be used as model systems for the donor–acceptor interface in bulk heterojunction blends.

